Stochastic (STOCH)
Function Syntax
=STOCH(data, period) data(array):
Range of columns containing the date, Open, high, Low, close, volume data.period(number):
The number of periods (days) used to calculate the Stochastic Oscillator.
Returns:
A three-column array of dates and their corresponding %K and %D values.
Google Sheets Output Example
Below is an example of the resulting array when applying the custom STOCH() function in Google Sheets
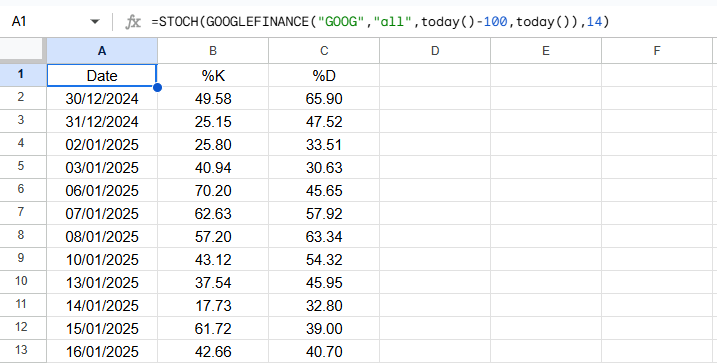
Apps Scripts Code
Here’s the full Google Apps Script code.
Paste this directly into the Google Sheets Apps Script editor (Extensions → Apps Script):
atr.gs
/**
* Calculates the Stochastic Oscillator for a given dataset and period.
*
* @param {array} data - a 2D array where the first column is the dates, and subsequent columns for open, high, low, close and volume.
* @param {number} period - The number of periods for calculating the Stochastic Oscillator.
* @returns {array} - A 2D array with headers: Date, %K, %D.
* @customfunction
*/
function STOCH(data, period) {
// Preprocess data using getData
const processedData = getData(data);
const dates = processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[0]); // Extract dates
const highs = processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[2]); // Extract high prices
const lows = processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[3]); // Extract low prices
const closes = processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[4]); // Extract close prices
// Check if the period is greater than the length of the data
if (period > closes.length) {
throw new Error("Error: The specified period exceeds the length of the data.");
}
// Calculate %K for each period
const kValues = [];
for (let i = period - 1; i < closes.length; i++) {
const periodHigh = Math.max(...highs.slice(i - period + 1, i + 1));
const periodLow = Math.min(...lows.slice(i - period + 1, i + 1));
const currentClose = closes[i];
const kValue = ((currentClose - periodLow) / (periodHigh - periodLow)) * 100;
kValues.push([dates[i], kValue]); // Store date and %K
}
// Calculate %D (3-period SMA of %K)
const dValues = SMA(kValues, 3).slice(1); // Calculate %D directly from %K and remove headers
// Align %K and %D lengths
const [alignedK, alignedD] = alignLENGTHS(kValues, dValues);
// Combine %K and %D values into final output
const stochValues = alignedK.map((k, i) => {
return [k[0], k[1], alignedD[i] ? alignedD[i][1] : null];
});
// Prepare the final data structure
return [["Date", "%K", "%D"], ...stochValues];
}
/**
*
* @param {Array<Array>} data - A 2D array of cell values to process. The first row should contain headers.
* @returns {Array<Array>} - A 2D array where the first row contains headers and subsequent rows contain processed data.
*
* @customfunction
*
*/
function getData(data) {
if (!data || data.length === 0) {
throw new Error("Input data is empty or invalid.");
}
// Check if the first row contains headers
const headers = Array.isArray(data[0]) && data[0].every(item => typeof item === "string")
? data[0]
: null;
if (!headers) {
// If no headers, assume the first column is the date column and process data
return data.map(row => row.map((value, index) => {
return index === 0 ? new Date(value) : parseFloat(value);
}));
}
// Process rows with headers
return [headers, ...data.slice(1).map(row => headers.map((header, index) => {
const key = header.toLowerCase();
return key === "date" ? new Date(row[index]) : parseFloat(row[index]) || row[index];
}))];
}
/**
* Calculates the Simple Moving Average (SMA) for a given dataset and period.
*
* @param {Array} data A range containing date and close price data from Googlefinance(), with no header row.
* @param {number} period The number of periods to calculate the SMA, e.g., 14 for a 14-day SMA.
* @returns {Array<Array>} The Simple Moving Average (SMA) of the range.
* @customfunction
*/
function SMA(data, period) {
const processedData = getData(data);
const dates = processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[0]); // Extract dates
const closePrices = processedData[0].length === 2
? processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[1]) // For 2-column arrays, use the second column
: processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[4]); // Default: use index 4 for close price
// Check if the period is greater than the length of the data
if (period > closePrices.length) {
throw new Error("Error: The specified period exceeds the length of the data.");
}
// Initialize an array to store SMA values with corresponding dates
let results = [["Date", `SMA(${period})`]]; // Include headers
// Calculate SMA for the given period
for (let i = period - 1; i < closePrices.length; i++) {
const periodPrices = closePrices.slice(i - period + 1, i + 1); // Get the slice for the period
const sma = periodPrices.reduce((acc, val) => acc + val, 0) / period; // Calculate average
// Append the current date and SMA to the results array
results.push([dates[i], sma]);
}
return results;
}
/**
* Aligns the lengths of two arrays by trimming the longer array to match the shorter one.
*
* @param {Array} arr1 - The first array.
* @param {Array} arr2 - The second array.
* @returns {Array} - An array containing two aligned arrays.
*/
function alignLENGTHS(arr1, arr2) {
const lengthDiff = arr1.length - arr2.length;
if (lengthDiff > 0) {
return [arr1.slice(lengthDiff), arr2];
} else if (lengthDiff < 0) {
return [arr1, arr2.slice(-lengthDiff)];
}
return [arr1, arr2];
}Last updated on