Standard Deviation (STDEV)
Function Syntax
=STDEV_INDICATOR(data, period) data(array):
Range of columns containing the date, Open, high, Low, close, volume data.period(number):
Number of (periods) days over which to calculate the Standard Deviation.
Returns:
A two-column array of dates and their corresponding Standard Deviation values.
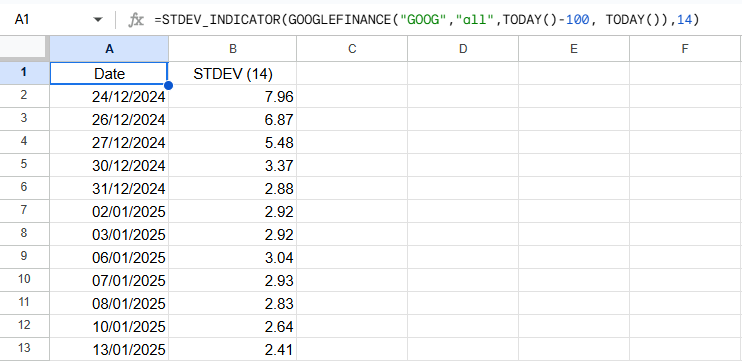
Google Sheets Output Example
Below is an example of the resulting array when applying the custom STDEV_INDICATOR() function in Google Sheets
Apps Scripts Code
Here’s the full Google Apps Script code.
Paste this directly into the Google Sheets Apps Script editor (Extensions → Apps Script):
stdev_indicator.gs
/**
* Calculates the Standard Deviation for raw price data using the SMA function.
*
* @param {array} data - an array where the first column is the dates, and subsequent columns for open, high, low, close and volume.
* @param {number} period The period for calculating the Standard Deviation.
* @returns {array} - an array with dates corresponding and the stdev values
* @customfunction
*/
function STDEV_INDICATOR(data, period) {
//Check number of arguments
if (arguments.length !== STDEV_INDICATOR.length) {
throw new Error(`Wrong number of arguments. Expected ${STDEV_INDICATOR.length} arguments, but got ${arguments.length} arguments.`);
}
// Preprocess data using getData
const processedData = getData(data);
const dates = processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[0]); // Extract dates
const closePrices = processedData[0].length === 2
? processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[1]) // For 2-column arrays, use the second column
: processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[4]); // Default: use index 4 for close price
// Check if the period is greater than the length of the data
if (period > closePrices.length) {
throw new Error("Error: The specified period exceeds the length of the data.");
}
// Calculate the SMA for the given period
const smaValues = SMA(data, period).slice(1); // Remove headers, format: [Date, SMA]
// Initialize an array to hold standard deviation values
const stdevValues = [["Date", `STDEV (${period})`]];
// Calculate moving standard deviation for each data point
for (let i = period - 1; i < closePrices.length; i++) {
const mean = smaValues[i - (period - 1)][1]; // Use SMA value as the mean
const periodPrices = closePrices.slice(i - period + 1, i + 1); // Get the prices for the period
// Calculate the squared differences
const squaredDifferences = periodPrices.map(val => Math.pow(val - mean, 2));
// Calculate the variance
const variance = squaredDifferences.reduce((acc, val) => acc + val, 0) / period;
// Calculate the standard deviation
const standardDeviation = Math.sqrt(variance);
// Append the results with the corresponding date
stdevValues.push([dates[i], standardDeviation]);
}
return stdevValues;
}
/**
*
* @param {Array<Array>} data - A 2D array of cell values to process. The first row should contain headers.
* @returns {Array<Array>} - A 2D array where the first row contains headers and subsequent rows contain processed data.
*
* @customfunction
*
*/
function getData(data) {
if (!Array.isArray(data) || data.length === 0) {
throw new Error("Input data must be a non-empty array.");
}
// Check if the first row contains headers
const headers = Array.isArray(data[0]) && data[0].every(item => typeof item === "string")
? data[0]
: null;
if (!headers) {
// If no headers, assume the first column is the date column and process data
return data.map(row => row.map((value, index) => {
return index === 0 ? new Date(value) : parseFloat(value);
}));
}
// Process rows with headers
return [headers, ...data.slice(1).map(row => headers.map((header, index) => {
const key = header.toLowerCase();
return key === "date" ? new Date(row[index]) : parseFloat(row[index]) || row[index];
}))];
}
/**
* Calculates the Simple Moving Average (SMA) for a given dataset and period.
*
* @param {array} data - an array where the first column is the dates, and subsequent columns for open, high, low, close and volume.
* @param {number} period The number of periods to calculate the SMA, e.g., 14 for a 14-day SMA.
* @returns {Array<Array>} The Simple Moving Average (SMA) of the range.
* @customfunction
*/
function SMA(data, period) {
//Check number of arguments
if (arguments.length !== SMA.length) {
throw new Error(`Wrong number of arguments. Expected ${SMA.length} arguments, but got ${arguments.length} arguments.`);
}
const processedData = getData(data);
const dates = processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[0]); // Extract dates
const closePrices = processedData[0].length === 2
? processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[1]) // For 2-column arrays, use the second column
: processedData.slice(1).map(row => row[4]); // Default: use index 4 for close price
// Check if the period is greater than the length of the data
if (period > closePrices.length) {
throw new Error("Error: The specified period exceeds the length of the data.");
}
// Initialize an array to store SMA values with corresponding dates
let results = [["Date", `SMA(${period})`]]; // Include headers
// Calculate SMA for the given period
for (let i = period - 1; i < closePrices.length; i++) {
const periodPrices = closePrices.slice(i - period + 1, i + 1); // Get the slice for the period
const sma = periodPrices.reduce((acc, val) => acc + val, 0) / period; // Calculate average
// Append the current date and SMA to the results array
results.push([dates[i], sma]);
}
return results;
}Last updated on